
histolytica, as it does in model organisms. There are several enzymes that have the nuclear localization signal: one phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) kinase, two PI 3-phosphatases, and one PI 5-phosphatase this suggests that PI metabolism also has conserved roles related to nuclear functions in E. Instead, homologs of class I PI 3-kinases and PTEN, a PI 3-phosphatase, exist as multiple isoforms, which likely reflects that elaborate signaling cascades mediated by PtdIns(3,4,5)P 3 are present in this organism. Additionally, regulatory subunits of class I PI 3-kinases and type III PI 4-kinases have not been identified. However, class II PI 3-kinases, type II PI 4-kinases, type III PI 5-phosphatases, and PI 4P-specific phosphatases are not present. It has a panel of evolutionarily conserved enzymes that generate all the seven PI species. histolytica appears to have 10 PI kinases and 23 PI phosphatases. histolytica via a genome-wide survey of the current genomic information.
#MTMR INHIBITOR FULL#
In this review, we summarized the full repertoire of the PI kinases and PI phosphatases found in E.
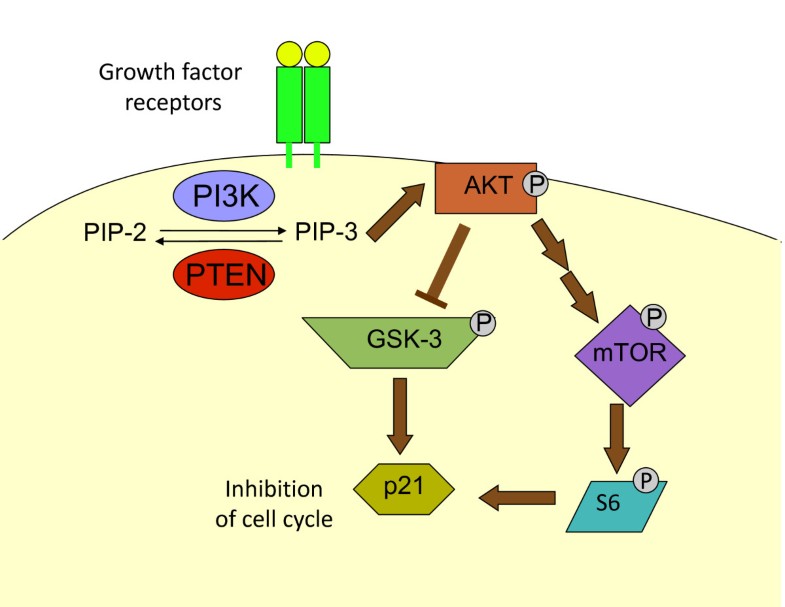
In contrast, the conservation of the enzymes that metabolize PIs in this organism has not been well-documented. histolytica is similar to that in mammalian cells, suggesting that PIs have orthologous functions in E. In the enteric protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica, it has been previously shown that the PIs phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PtdIns3P), PtdIns(4,5)P 2, and PtdIns(3,4,5)P 3 are localized to phagosomes/phagocytic cups, plasma membrane, and phagocytic cups, respectively. Each of the seven PIs has a unique subcellular and membrane domain distribution. Phosphoinositides (PIs) are phosphorylated derivatives of PtdIns and consist of seven species generated by reversible phosphorylation of the inositol moieties at the positions 3, 4, and 5. Phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) metabolism is indispensable in eukaryotes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
